6.React UI库
material-ui(国外)
ant-design(国内蚂蚁金服)(推荐)
下载antd
npm i antd --save在引入的时候,不要忘记也要引入 antd/dist/antd.css(官网显示代码居然没有提示要引入css),不过最好要按需引入,import 'antd/dist/antd.css'加载了全部的 antd 组件的样式 。
不过现在好像结合webpack的tree shaking,自动按需引入了,不用管
此时我们可以进入官网 -> 文档-> 在create-react-app ->高级配置中使用进行查看(看不到就看3.x版本)
假如我只是用了Button组件
//引入Button组件
import { Button } from 'antd'
import 'antd/dist/antd.css'Vue的话推荐使用element-UI库,后面反响不错,也出了react的UI
关于eject之后antd的主题颜色配置
由于私自eject了,官网没有相关eject后的主题配置的代码,在网上翻来覆去,终于找到真正合适的文章
https://blog.csdn.net/f980815/article/details/109385835
对于React Native的按需导入,还得再babel.config.js进行配置
npm i ant-design/react-nativemodule.exports = {
presets: ['module:metro-react-native-babel-preset'],
// 按需加载
"plugins": [
["import", { libraryName: "@ant-design/react-native" }] // 与 Web 平台的区别是不需要设置 style
]
};7.redux
redux是一个专门做状态管理的JS库(集中式管理)
它可以在React、Angular、Vue等项目中,但基本和React配合使用
- 作用:集中式管理react应用中多个组件共享状态
- 当需要大量共享可以使用,但是能不用就不用,毕竟是全局的东西
(实际上有点像Vuex,Vue人家就很少用这个,用自己内部的Vuex)
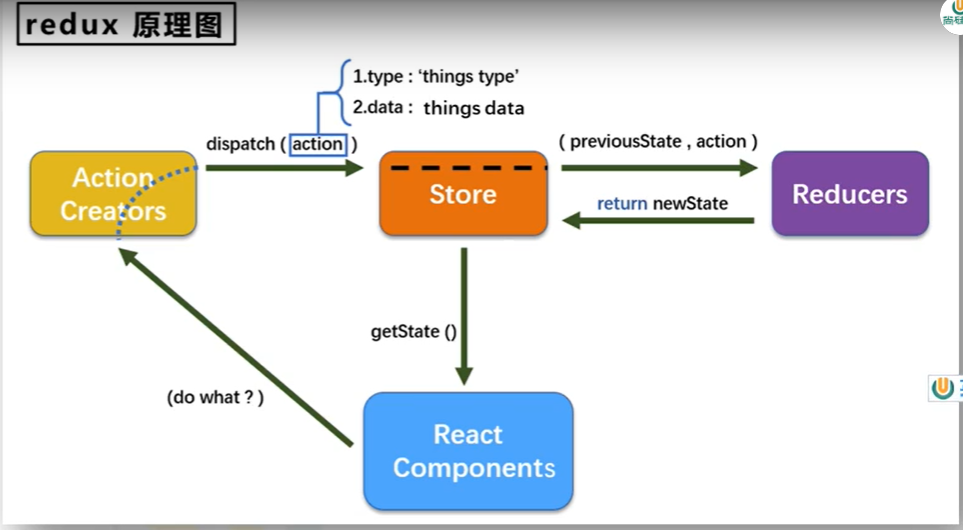
以上为redux原理图
redux三个核心概念
action
有同步action (sync)和异步action (async)
- 动作对象
- 包含两个属性:
- type:标识属性,值为字符串,唯一,必要属性
- data:数据属性,任意类型,可选属性
reducer
Reducers不仅能加工状态(加工状态那么部分有点像Vue里的mutations),还能初始化状态
加工时,根据旧的state和action,产生新的state纯函数
在初始化时,reducer得到的previousState、action分别为 undefined、type:'@@init' + 随机字符,data: 无
store
将state、action、reducer联系在一起的对象,负责对外暴露
基本使用
初始化
npm i redux新建一个redux文件夹
- 新建 store.js
- 新建一个处理xxx组件的 xxx-reducer.js
- 可选,新建一个处理xx组建的xxx-action.js
建立store
store.js是专门用于暴露一个store对象,整个一应用只有一个store对象,配合redux的createStore API 可以创建一个store对象
//store.js
//createStore专门用于创建store对象
import { createStore } from 'redux'
// 引入reducer
import countReducer from './count_reducer'
// 暴露store
export default createStore(countReducer)createStore
- 第一个参数传入reducer
- 第二个参数可选,传入state的默认状态,当然state的默认值也可以通过给reducer的第一个参数赋值上默认值来确定
关于store的小bug
由于全局状态store是保存在内存中的,如果刷新当前页面,则我们之前通过action调用reducer对store做的修改都从零开始
建立reducer
这里我模拟一个处理count数据的reducer
xxx_reducer.js是用于创建一个为Count组件服务的reducer,reducer的本质就是一个函数,reducer函数会接到两个参数,分别为:之前的对象preState、动作对象action
// reducer用于最基本的数据处理,是一个纯函数,其实是为了diff算法
const initState = 0;
//如果你要存多个数据,可以初始化成一个对象
export default function countReducer(preState = initState, action) {
console.log(preState);
const { type, data } = action;
let newState = preState;
switch (type) {
case 'increment':
return newState + data * 1;
case 'decrement':
return newState - data * 1;
default:
// 不加也不减,说明是初始化
return newState
}
}在面对多人开发时,如果只用一个reducer,可能会堆积大量的状态,我们可以拆分reducer函数
import { combineReducers, createStore } from 'redux'
import CityReducer from './reducer/CityReducer'
import TabbarReducer from './reducer/TabbarReducer'
const reducer = combineReducers({
CityReducer,
TabbarReducer
})
export default createStore(reducer)而此时我们获取Store的时候,不能直接通过 getState,需要
console.log(store.getState().CityReducer)
console.log(store.getState().TabbarReducer)关于reducer的小bug
在redux底层会做一个判断,如果返回的东西,和之前的preState是一样的,那就不会进行页面更新。
注意redux的reducer必须是一个纯函数(纯函数的概念我在ES5篇章有提及到)
而对比vue,由于他用的是代理,所以复杂数据类型怎么改也不会影响到原来的数据
export default function personReducer(preState = initState, action) {
const { type, data } = action;
switch (type) {
case ADD_PERSON:
// 做了一个浅比较,返回的preState的地址值和之前的是一样的,那就不进行页面更新了
//错×:preState.unshift(data); return preState;
return [data, ...preState]
default:
return preState;
}
}所以可以在React、Redux里面,我们很少使用push、unshift这些数组方法,而且这样会导致函数不再是纯函数了。
关于store的更新
// 引入store,用于获取redux中保存的状态
import store from '../redux/store'
//可以直接获取store存储的数据
console.log(store.getState())这里我直接在组件内自定义increment函数模拟action向store发送更改 数据的类型type 和 传入的数据data
increment = () => {
const { value } = this.selectNumber;
// dispatch传入type和data
store.dispatch({ type: 'increment', data: value });
}但是平时我们使用setState会自动帮我们调用一次render更新页面,但是store更新没有调用render
解决方法一:在组件内,在componentDidMount生命周期钩子后使用 redux 带的 subscribe API ,用于订阅状态更改,监听store数据的变化,发生变化则执行传入的回调函数( this.setState({}) -> render )
// DOM挂在完毕后,监听redux中状态的变化,只要变化就调用render
componentDidMount() {
store.subscribe(() => {
//虚晃一枪,让它帮我们调用一次render(自己调用this.render不管用)
//不过我感觉使用forceUpdate()好像也行
this.setState({});
})
}如果是hook组件,则
useEffect(() => {
const unSubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
setState(store.getState())
})
return () => {
unSubscribe()
}
}, [])但是这种订阅方式,必须让组件销毁时,将其也取消订阅,不然会重复订阅,因为store.subscribe不会随着组件被销毁而消失,而是默默保存在redux的内部订阅者数组中
store.subscribe会返回一个函数,该函数时取消订阅的(在类式组件中可以在 componentWillUnmount 中取消订阅 )
useEffect(() => {
const unSubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {})
return () => {
unSubscribe()
}
}, [])解决方法二:对于整个组件,直接用redux 带的 subscribe API 进行包裹,(这里老师说有了diff算法,实际上整体性能影响不会特别大)
//ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.querySelector('#root'));
store.subscribe(() => {
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.querySelector('#root'))
})解决方法三:使用react-redux
补充Action
此时可以补充action提交修改:向store发送更改 数据的类型type 和 传入的数据data
在redux文件夹下创建xxx_action.js,导出action方法
export const createIncrementAction = data => ({ type: 'increment', data });
export const createdecrementAction = data => ({ type: 'decrement', data });然后可以直接在组件中导入 + 使用,可以像官方redux原理图一样,不需要自己来 向store发送更改 数据的类型type 和 传入的数据data
和Vue一样,开发时定义常量是减少错误的基本方法(实际上也是防止单词写错)
然后再组件中使用Action方法
import { createIncrementAction } from '../redux/count_action'increment = () => {
const { value } = this.selectNumber;
// dispatch为action传入参数
store.dispatch(createIncrementAction(value));
}async Action
action可以为对象(type、data属性),也可以为函数
我们返回一个函数,把异步操作存放在这个函数里,再调用同步action(异步Action中一般都会调用一个同步action),由此形成一个异步操作,
因为store只认action作为一个对象来返回,此时我们需要用到一个中间件,让store愿意接收一个函数,并且调用它:(即使我们在异步action中写明了直接return对象,但是也由于异步的原因,函数体执行完毕了,直接返回一个undefined)
除了redux-thunk之外,redux-promise中间件也是一种实现异步action的方式,直接返回一个promise
npm i redux-thunk然后再store.js里
//store.js
//applyMiddleware为store使用中间件的API
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
// 引入reducer,thunk为接收函数式action必须的中间件
import Reducer from './reducer'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
// 暴露store,
export default createStore(Reducer, applyMiddleware(thunk))然后在action.js这个文件里定义异步action(作为一个函数返回,经过中间件的处理,接收一个dispatch方法,可帮助你调用同文件下的同步action方法)
export const asyncIncrement = (data) => {
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(() => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(data))
}, 1000);
}
}在组件中使用:
import store from '../redux/store'
import {asyncIncrement } from '../redux/count_action'store.dispatch(asyncIncrement(value, 500));异步action:它不是一个必须的东西,实际上我们可以在自己的组件函数里定义异步操作,只是当你不想要把异步操作放在组件里是,可以使用以上异步action方法
redux-thunk原理
export default function thunkMiddleware({ dispatch, getState }) {
return (next) => (action) =>
typeof action === "function" ? action(dispatch, getState) : next(action);
}redux-saga
redux-saga解决异步actions问题
maybe看不惯了把原来作为对象的action变成了其他形式,于是后面出了一个redux-saga,其原理是使用了生成器(generator)
在saga中,全局监听和接收器使用Generator函数和saga自身一些辅助函数实现对整个流程的管控
npm i redux-saga在redux下新建一个saga.js文件
import { take, fork, call, put } from "redux-saga/effects";
/*
function* watchaSaga() {
while (true) {
//take监听组件
yield take("getList");
//fork同步执行异步处理函数(非阻塞式)
yield fork(GetList);
}
}
*/
//watchSaga另外一种写法
function* watchaSaga() {
yield takeEvery("getList", GetList)
}
function* GetList() {
// 异步处理
//call函数发异步请求,传入一个返回值为promise对象的函数,阻塞式调用
let res = yield call(asyncGetList);
// put函数发出新的action
yield put({
type: "changeList",
payload: res,
});
}
function asyncGetList() {
return new Promise((res, rej) => {
setTimeout(() => {
res("返回结果");
}, 2000);
});
}
export default watchaSaga;此时在store.js中,嵌入中间件,并且在导出store之前调用watchSaga进行实时监听
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import createSagaMiddleWare from "redux-saga";
import countReducer from "./reducer";
import watchSaga from "./saga";
// 和redux-thunk一样,都要套入中间件
const SagaMiddleWare = createSagaMiddleWare();
const store = createStore(countReducer, applyMiddleware(SagaMiddleWare));
SagaMiddleWare.run(watchSaga);
export default store;然后再reducer中照常监听dispatch传过来的type和payload
interface IAction {
type: string;
payload?: any;
}
interface IPreState {
isShow: boolean;
list: string;
}
export default function countReducer(
preState: IPreState = {
isShow: true,
list: "",
},
action: IAction
) {
const { type, payload } = action;
let newState = preState;
//...
switch (type) {
case "changeList":
console.log("enter changelist");
newState.list = payload;
return newState;
default:
return preState;
}
}最后在组件中使用时,直接dispatch在saga.js中监听的type
store.dispatch({type: 'getList', payload: 'nothing'})(大火看到redux-thunk的好了吧?。。)
小redux
个人小小小版redux赏析
function createStore(reducer, initialState = {}) {
//用于存放订阅者
const list = [];
let state = reducer() | initialState;
function subscribe(callback) {
list.push(callback);
}
function dispatch(action) {
reducer(state, action);
for (let i in list) {
list[i] && list[i]();
}
}
function getState() {
return state
}
return {
subscribe,
dispatch,
getState,
};
}8.react-redux
facebook为了让开发人员更加舒服使用redux,开发了react-redux
(其实我个人觉得可以理解为,react让组件和redux之间的交互多了一个中间人(套了个外壳):container,使得我们以后都不需要关心订阅和取消订阅的问题)
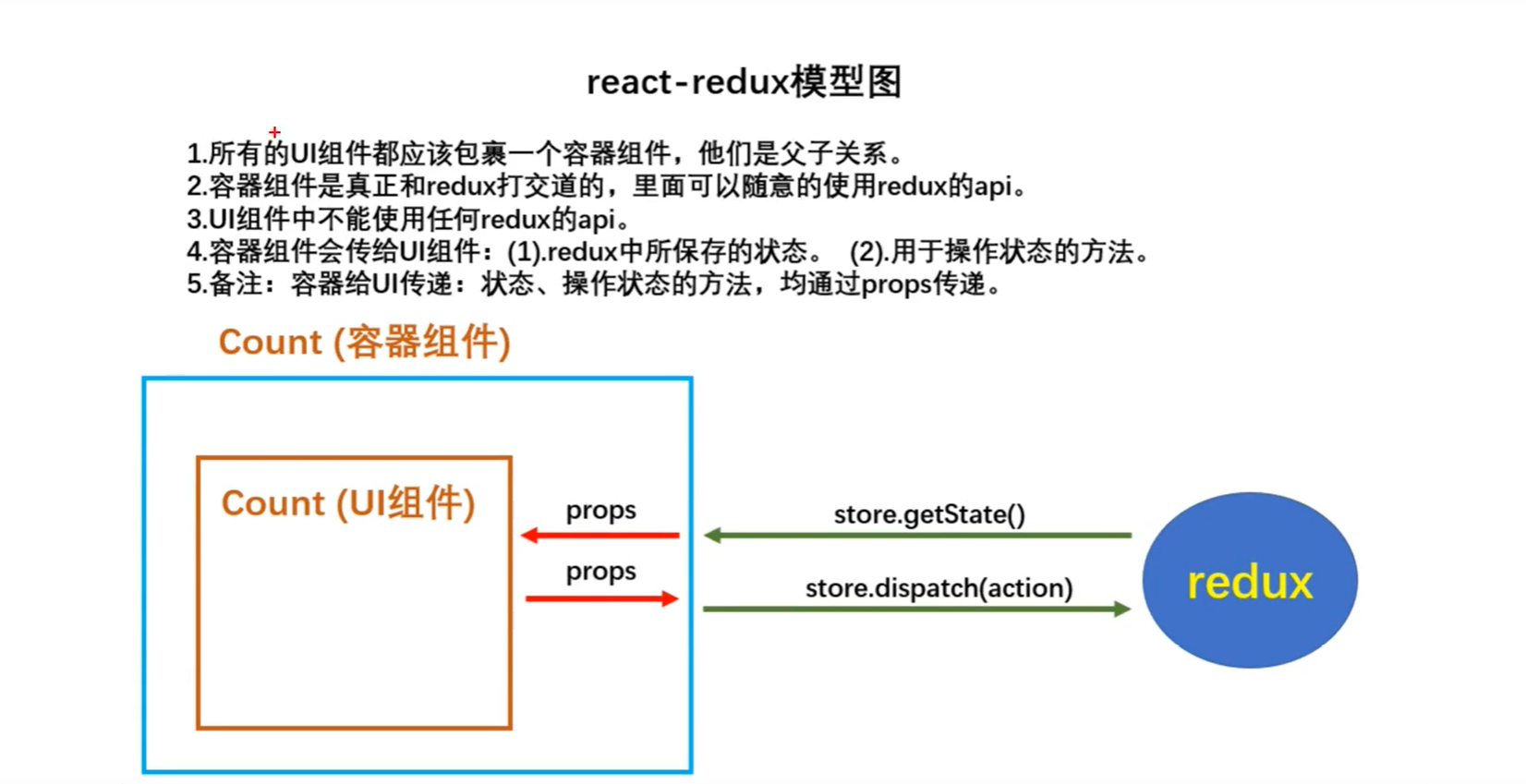
可以看得出外面要了一层容器,防止UI组件直接对接redux
components文件夹存放的是UI组件(不能使用任何的redux API,只负责页面的呈现)
我们要创建一个container的文件夹,然后新建一个容器组件,容器组件作为UI组件 和 react-redux的桥梁,不能直接rcc自定义组件,而是使用react-redux库创建。
npm i react-redux连接UI
连接UI组件的方式:新建一个containers文件夹,index.jsx文件
// 引入CountUI组件,CountUI组件为components文件夹下的自定义组件
import Count from '../../components/Count'
// 引入connect用于连接UI组件和redux
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
// 使用connect()()创建并且暴露一个Count容器组件
export default connect()(Count)亦或者在导出UI组件的时候,直接
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
export default connect()(组件名)连接store
此时把原来引入UI组件替换成容器的自定义组件
连接store的方式:在app组件使用容器组件时,通过定义属性props方式对 Count 容器 传入store(之前是导入 store后 ,通过 store.getState()获取数据的 )
import React, { Component } from 'react'
//import Count from './components/Count' //现在不需要在app.jsx文件里直接导入UI组件
import Count from './containers/Count' //而是需要导入container组件
import store from './redux/store'
export default class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<Count store={store} />
</div>
)
}
}优化
连接store的方式为 在组件中传入store作为props属性<Count store={store},如果多个容器组件,岂不是要一个一个传?不用,react-redux里有个 Provider组件,用 provider组件 将外壳app组件包裹住,则在整个应用里面,但凡需要store的容器组件,都会传过去
//总的index.js文件
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom'
import App from './App'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import store from './redux/store'
//此处使用Provider,使得APP的所有后代容器组件都能接收store
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>, document.querySelector('#root'));此时我们在ui组件可以直接通过props接收
connect的第一个参数可以接收一个回调函数(mapDispatchToProps),回调函数则会传入store的数据作为参数,在回调函数返回值中,亦可以自定义一些props的参数
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
function Index(props) {
console.log(props.isShow)
}
export default connect((state) => {
return {
a: 1,
isShow: state.TabbarReducer.show
}
})(Count)容器和UI的交互
由于容器组件的创建比较不走寻常路,所以它传递给子组件(UI组件)props的方式也有点不寻常
在连接UI组件时使用到的connect API,可以传入两个参数,并且得传两个函数(mapStateToProps函数、mapDispatchToProps函数)作为参数 。(在上方react-redux模型图可以看到第一个参数传状态,第二个参数传方法)
mapStateToProps(函数)
1.mapStateToProps函数的返回值是一个对象
2.作为状态(key: value 组合的对象)传递给UI组件
3.通过props传入store,使得第一个参数的函数默认传入store的state状态作为参数(state = store.getState())
mapDispatchToProps(函数)
1.mapDispatchToProps函数的返回值是一个对象
2.作为操作状态的方法(key: func 包含函数的对象)传递给UI组件
3.通过props传入store,使得第二个参数的函数默认传入store的dispatch方法,直接使用dispatch告诉action你要执行的事件
//count组件的父容器的index文件
// 引入CountUI组件
import CountUI from '../../components/Count'
// 引入connect用于连接UI组件和redux
import { connect } from 'react-redux'
// 引入redux中的action提交对状态的修改
import { createIncrementAction, asyncIncrement, createdecrementAction } from '../../redux/count_action'
function mapStateToProps(state) {
return { count: state } //假如state = 900,相当于正常父子组件传值 <CountUI count={900}>
}
function mapDispatchToProps(dispatch) {
return {
increment: (number) => {
dispatch(createIncrementAction(number))
},
decrement: (number) => {
dispatch(createdecrementAction(number))
},
asyncIncrement: (number, time) => {
dispatch(asyncIncrement(number, time))
}
}
}
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(CountUI)然后我们在子组件(UI组件),就可以直接通过props.xx获得传入的状态/修改状态的方法,对子组件进行操作修改
优化:
.对于上述mapDispatchToProps 的精简写法:
在写mapDispatchToProps部分的时候,react-redux会帮你做一个自定分发的动作(自动dispatch)
也就是判断当前是否为action,如果是就自动跑分发dispatch的逻辑;如果不是按照以往的代码逻辑执行
export default connect(
state => ({count:state}),
//原本mapDispatchToProps函数变成一个对象(key: action)
{
increment: createIncrementAction,
decrement: createdecrementAction,
asyncIncrement: asyncIncrement,
}
)(CountUI)//ui组件中使用
const { count } = this.props;
increment = () => {
const value = parseInt(this.selectNumber.value);
this.props.increment(value);
}我们自己对文件的优化:
由于每个UI组件为了对接redux存储的状态,都会多一个容器组件,导致文件量成倍增长。
所以我们可以自己把容器组件和UI组件写在同一个jsx文件里,对外暴露容器组件
react-redux原理
connect是HOC,高阶组件
Provider组件,可以让容器组件拿到state,使用了context
小react-readux的connect
function myConnect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) {
return (myComponent) => {
return (props) => {
return <div>
<myComponent {...mapStateToProps} {...props} {...mapDispatchToProps}></myComponent>
</div>
}
}
}9.其他
Redux DevTools
这里顺便推荐一下redux的相关开发者工具:Redux DevTools(这个工具很顶阿!)(React的开发者工具React Developer Tools也推荐安装),在谷歌商店添加拓展插件即可
但是使用这个工具还得安装拓展库
npm i redux-devtools-extension别忘了还要再store.js文件中导入 + 使用
可以在官网查看https://github.com/zalmoxisus/redux-devtools-extension
关于react-redux数据持久化,可以使用redux-persisthttps://github.com/rt2zz/redux-persist
immutable
除此之外,我在《JavaScript进阶ES5》中还提及到关于很适用于reducer纯函数系列的js库 immutable.js,它的实现原理是persistent data structure(持久化数据结构),也就是使用旧数据创建新数据时,保证旧数据同时可用且不变,同时避免了deepcopy把所有的节点都复制一遍带来的性能损耗,immutable使用了structural sharing(结构共享),即如果对象树中一个节点发生变化,只修改这个节点和受他影响的父节点,则其他节点进行共享
具体使用
npm i immutableimmutable对数组偏爱,可以直接让List当数组来使用,一般都可以调用数组上的所有方法,包括map、filter、shift之类的
import { Map, List } from 'immutable'
const obj = {
name: "allen",
age: 18
}
const arr = []
const oldImmuObj = Map(obj) //转化为一个不可变对象
const oldImmuArr = List(arr) //转化为一个不可变对象,数组用List,对象用Map
const newImmuObj = oldImmuObj.set("name", "Mikasa")//此时新值的改动不会影响到老的值
const newImmuArr = oldImmuArr.push(1)//数组直接改就好了在 immutable这种不可变对象中,获取属性值可以使用
- get方法直接获取
oldImmuObj.get("name")
- 不可变对象再转换回普通对象
oldImmuObj.toJS()
- 数组不可变对象转换回数组
oldImmuArr.toJS()
如果数据类型更加复杂了,还得往里面继续包裹,才能打造成那种拷贝后仍共享的结构
import { Map } from 'immutable'
const a = Map({
name: "allen",
hobbies:Map({
name: 'killing'
})
})既然如此,每一次复杂数据类型都要包裹一次这么麻烦干嘛还要用它?有什么意义?
比如上方的name给组件A使用,如果name发生改变,shouldComponentUpdate应该返回true;而hobbies给组件B用,通过自己写代码(用if语句)判断无变化,让shouldComponentUpdate返回false,避免了diff重复对比(不过我个人感觉这有点太忒麻烦。。。)
除了每一次对复杂数据类型使用 Map、List包裹,还能使用fromJS,直接深度遍历,一次性转换好
它的效果和使用Map、List一层一层包裹是一样的
import { fromJS } from 'immutable'
const a = fromJS({
name: "allen",
hobbies:{
name: 'killing'
}
})修改深层属性值的时候使用 setIn 方法
a.setIn(["hobbies", "name"], 'swimming')修改数组的话是这样
arr.updateIn(["favor"], (list) => list.splice(index, 1))此时再结合reducer,这样的话react UI部分就不用修改了
export default function Reducer(preState = {
name: "allen",
hobbies:{
name: 'killing'
}
}, action) {
const { type, data } = action;
const newState = fromJS(preState)
switch (type) {
case "changeHobbies":
return newState.setIn(["hobbies", "name"], 'swimming').toJS()
default:
return preState;
}
}

